Development Regulations: A Comprehensive Guide
Development Regulations: A Comprehensive Guide
Development Regulations: A Comprehensive Guide
Development Regulations: A Comprehensive Guide
Why Are Development Regulations Necessary?
The primary purpose of development regulations is to allow local and national authorities to regulate and control land and property markets, ensuring the integration of complementary land uses. By designating specific uses for different sites, development regulations provide a framework for shaping the layout of towns and cities and facilitating various types of development. Additionally, these regulations offer the opportunity to stimulate or slow down development in specific areas, aligning with the broader goals of urban planning.
The planning and zoning process varies across different regions, with some jurisdictions granting authority to local authorities like municipalities or counties, while others vest zoning control at the state or national level. In certain cases, a combination of these approaches is adopted. To supplement zoning regulations, additional measures may be employed, such as planning scheme overlays or impact assessments, which further influence and refine the zoning process.
Understanding Zoning Codes
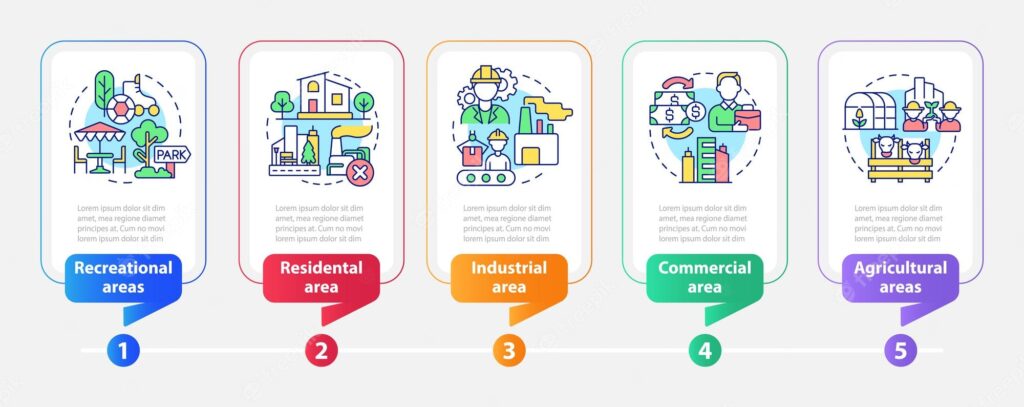
Zoning, a fundamental aspect of development regulations, involves the division of land within a jurisdiction into regulated zones. These designated zones dictate the permissible land uses and purposes, including residential, commercial, and transportation uses. Zoning also enables local governments to enforce protections for critical areas and other environmentally sensitive zones within their jurisdiction.
Zoning maps serve as visual representations of the various zones throughout a jurisdiction. It is important to note that the officially adopted zoning map, rather than a comprehensive plan’s “future land use map,” governs the specific permitted uses and development restrictions for individual parcels of land. However, it is essential for the zoning map to align with the comprehensive plan to ensure consistency and coherence in the planning process.
Examples of City Zoning Codes
To provide a clearer understanding of zoning codes, let’s explore a few examples from different cities:
Bellingham Zoning Map
: The zoning map of Bellingham provides a standard version of city zoning, offering insights into the various zoning districts and their respective regulations.
• Link: Bellingham Zoning Map
Lacey Zoning Map
: Lacey’s zoning map is presented through a GIS application, allowing users to interactively explore the developed zoning map.
• Link: Lacey Zoning Map
Whatcom County Zoning Map
: Whatcom County provides a comprehensive zoning map, showcasing the large-scale division of diverse land uses within the county.
• Link: Whatcom County Zoning Map
Examples of County Zoning Codes
Let’s also consider a few examples of county-level zoning codes:
Example County Zoning Code 1
: This county zoning code illustrates the specific regulations and requirements for land use and development within its jurisdiction.
• Link: Example County Zoning Code 1
Example County Zoning Code 2
: Another county zoning code provides a different perspective on land use regulations, catering to the unique needs of its jurisdiction.
• Link: Example County Zoning Code 2
These examples highlight the diversity and complexity of zoning codes, underscoring the importance of understanding the specific regulations within a given jurisdiction.
Unified Development Codes: Integration and Streamlining
Unified Development Codes (UDCs) offer a streamlined approach to land use and development regulations by integrating multiple types of regulations into a single code document. UDCs often combine zoning codes, subdivision regulations, critical areas ordinances, and development review procedures, providing a comprehensive framework for land use control.
Examples of City UDCs
To illustrate the concept of Unified Development Codes, let’s explore a couple of examples from different cities:
Example City UDC 1
: This city’s UDC encompasses various land use and development regulations, consolidating them into a unified document for ease of reference and compliance.
• Link: Example City UDC 1
Example City UDC 2
: Another city’s UDC adopts a similar approach, integrating different regulations within a single code to ensure efficient land use management.
• Link: Example City UDC 2
These examples demonstrate the benefits of employing Unified Development Codes, streamlining the regulatory process and enhancing clarity for developers and stakeholders.
Development Review Procedures: A Guide to Efficient Permitting
In addition to zoning and development codes, many municipal and county jurisdictions have separate chapters or sections dedicated to development review procedures. These procedures outline the processes, procedures, and timelines for reviewing and approving/denying new development proposals and other relevant permits. They also define staff roles, permit requirements, and noticing procedures.
Examples of Development Review Procedure Codes
To gain insights into the structure and content of development review procedure codes, let’s explore a few examples:
Example Municipal Code Ch. 17.77
: This code chapter provides an example of streamlining permit review processes for specific permit and development types, such as wireless infrastructure, subdivisions, and building permits.
• Link: Example Municipal Code Ch. 17.77
Example Municipal Code Ch. 18.04
: The development review procedures in this municipal code are organized into different levels based on development or permit type, ensuring clarity and efficiency in the review process.
• Link: Example Municipal Code Ch. 18.04
Example County Code Title 16A
: This county code establishes review procedures for building and land permits, providing guidelines for a smooth and effective permitting process.
• Link: Example County Code Title 16A
These examples highlight the importance of well-defined development review procedures in facilitating efficient and transparent permit processing.
Moratoria and Interim Zoning Ordinances: Temporary Measures for Land Use Control
In certain circumstances, local governments may adopt moratoria or interim zoning ordinances to address specific land use issues. These temporary measures allow authorities to suspend or restrict land use activities while conducting further studies or formulating new regulations. However, it is important to note that moratoria or interim zoning cannot be used to designate or conserve critical areas, agricultural lands, forestlands, or mineral resource lands.
Examples of Moratoria
To understand the practical application of moratoria, let’s explore a few examples:
Example Emergency Ordinance No. 2020-03-006
: This emergency moratorium suspends the acceptance, processing, review, and issuance of land use or building applications or permits for the construction of new residential dwellings.
• Link: Example Emergency Ordinance No. 2020-03-006
Example Resolution 2021-101
: This resolution imposes a moratorium on the development or designation of short-term rentals while the county formulates regulations for this type of accommodation.
• Link: Example Resolution 2021-101
Example Code Sec. 40.260.80
: This code section establishes a moratorium on forest practices, limiting development in environmentally sensitive areas for conservation purposes.
• Link: Example Code Sec. 40.260.80
Example Code Ch. 18H.30
: This code chapter outlines the criteria and procedures for implementing a development moratorium, providing guidance for local governments in managing land use activities.
• Link: Example Code Ch. 18H.30
These examples showcase the diverse applications and purposes of moratoria, highlighting their role in temporary land use control.
Interim Zoning Regulations: Temporary Measures with a Purpose
Interim zoning regulations serve as temporary measures that establish emergency or provisional zoning while agencies allow applications or develop changes to existing zoning codes. These regulations are particularly relevant in situations where there is a need to address specific challenges or opportunities related to development projects.
To illustrate the concept of interim zoning regulations, let’s examine a couple of examples:
Example Ordinance No. 19-0547
: This interim zoning ordinance imposes a six-month prohibition on accepting applications for new residential/multi-family development in certain zones of the city.
• Link: Example Ordinance No. 19-0547
Example Ordinance No. 02012-019
: This emergency interim zoning ordinance introduces temporary zoning controls for a neighborhood, valid for a duration of 12 months.
• Link: Example Ordinance No. 02012-019
These examples demonstrate how interim zoning regulations can be employed to address specific development challenges or opportunities on a temporary basis.
Conclusion
Development regulations, including zoning codes, unified development codes, and development review procedures, play a critical role in shaping the built environment and ensuring the efficient management of land use activities. Moratoria and interim zoning ordinances provide temporary measures for addressing specific land use issues and facilitating the planning process. By understanding and effectively utilizing these development regulations, local governments can promote sustainable and well-planned urban development while stimulating private sector participation in urban regeneration projects.
Remember, every jurisdiction has its own unique set of development regulations, so it’s essential to consult the specific codes and ordinances applicable to your area for accurate and up-to-date information.